The main components in CT tube - cathode, anode, and bearing - can each be independently developed into a branch of a subject. This issue only briefly discusses the cathode part.
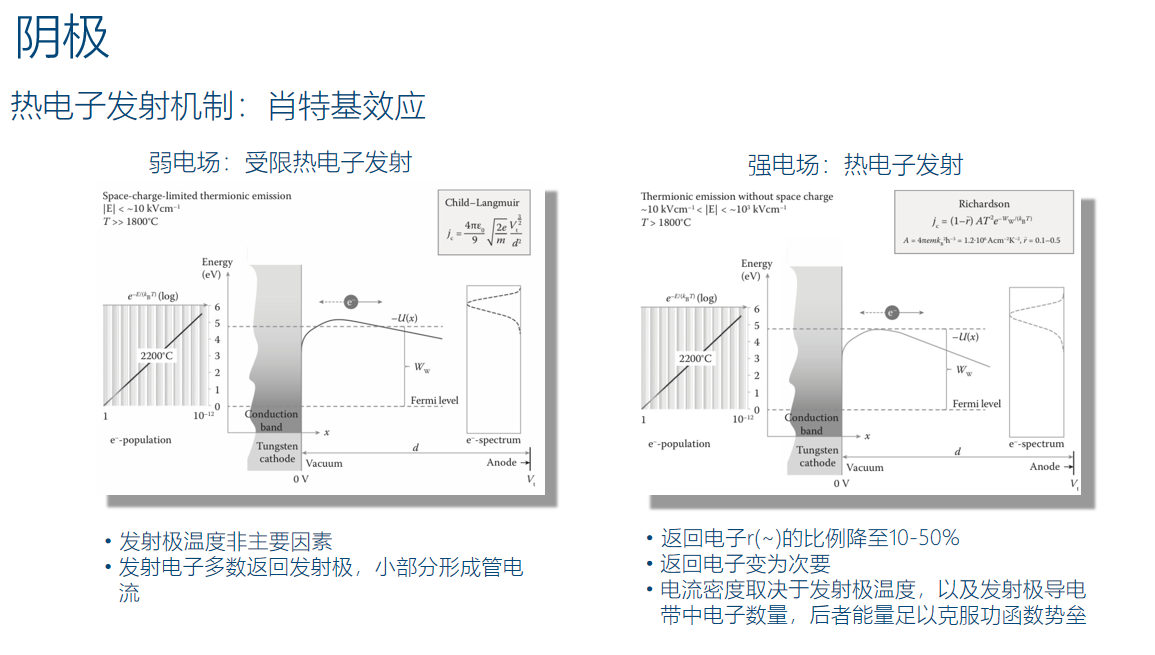
When working with a hot cathode, the main consideration is the influence of the electric field formed by space charges on the emission process. The relationship between emitter temperature, space charge, and the strength of the applied electric field becomes a constraint on the emission process.
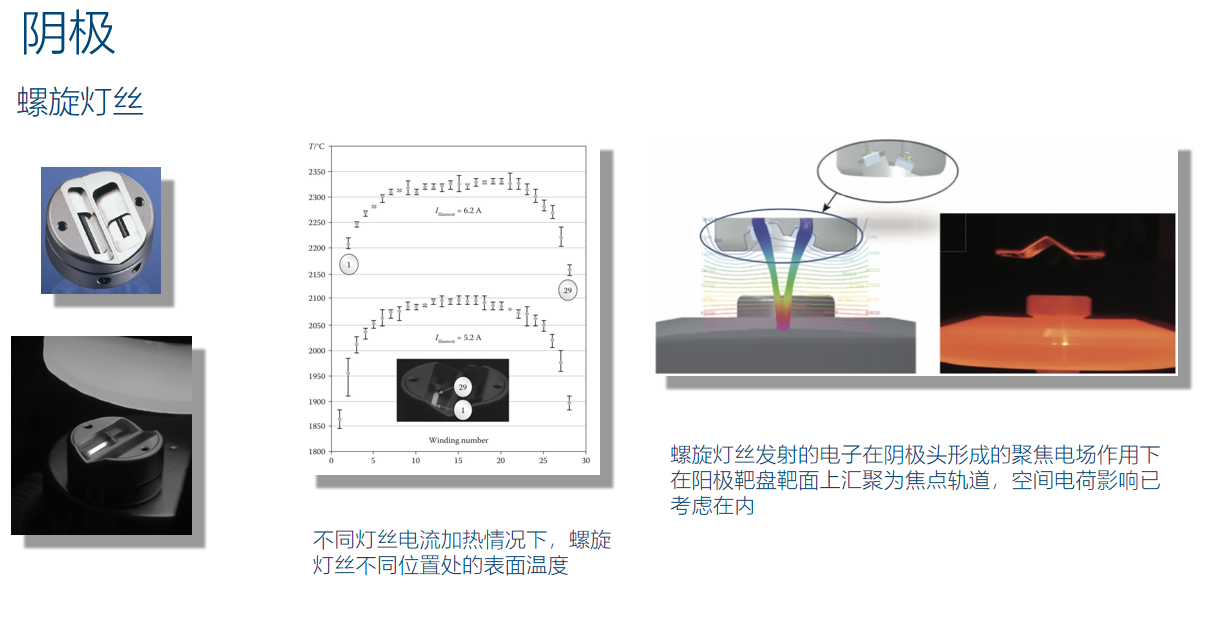
The speed of the contemporary CT machine frame is getting faster and faster, and the image acquisition time is shortened. In order to avoid “photon starvation” in relevant parts of the image, which can cause degradation, increasing the tube current has become a practical means. The conventional spiral filament can provide a tube current of about 300mA, while the flat filament tubes used in mid to high end CT tubes can have a current of up to 1000mA, even higher.

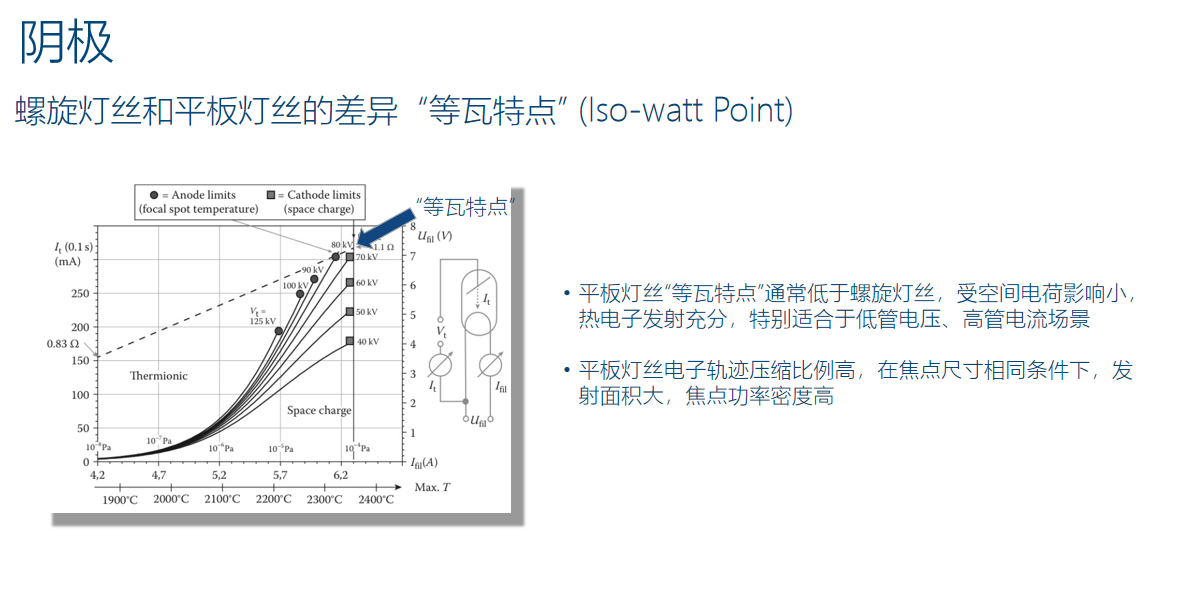
And combined with more complex conjugate coils (focus shaping) and deflection coils (electron beam flight trajectory bending or flying focus function), the restricted conditions of the cathode in CT tube are mainly influenced by the electric field formed by space charges, in addition to the inherent emission characteristics of the cathode material. Compared to spiral filaments, flat filaments have lower "equal wattage characteristics", more abundant hot electron emission, and higher focal power density.
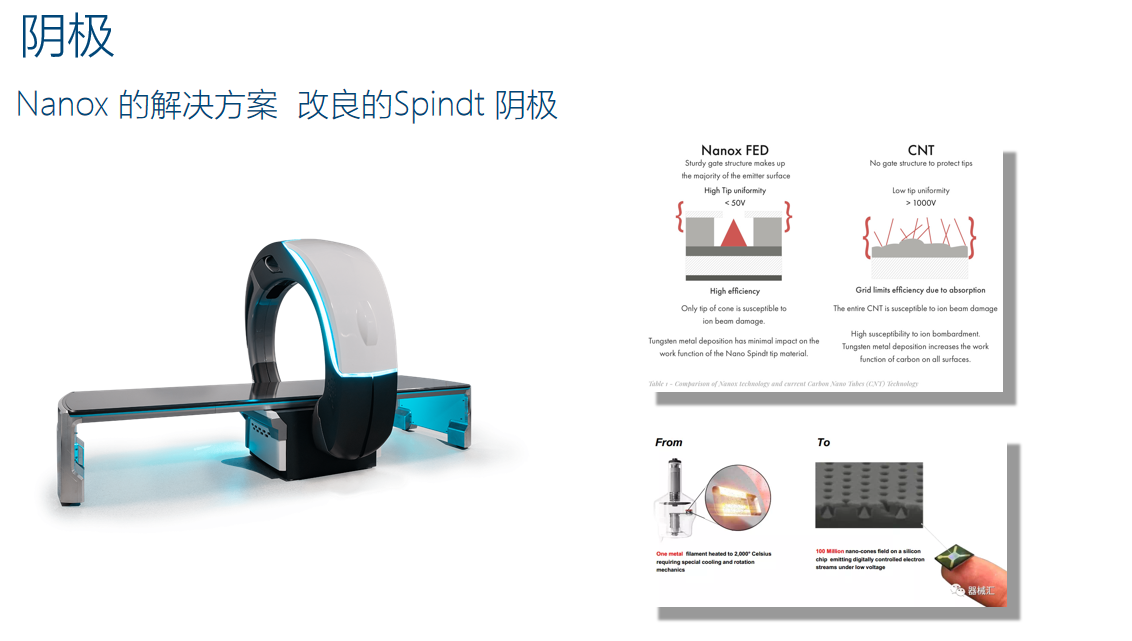
The "equal tile characteristics" can be understood as the "watershed" where the anode becomes a restricted condition or the cathode becomes a restricted condition in an X-ray tube. The "field emission effect" utilized by "cold cathode" is not a fresh concept. I have a book named "Vacuum Physics and Technology",which was published by the National Defense Industry Press in the 1980s, including a chapter on field emission. In the early stages of field emission, Spindt emission cone arrays were often used as the emitter, and currently, carbon nanotube structures are mainly used.
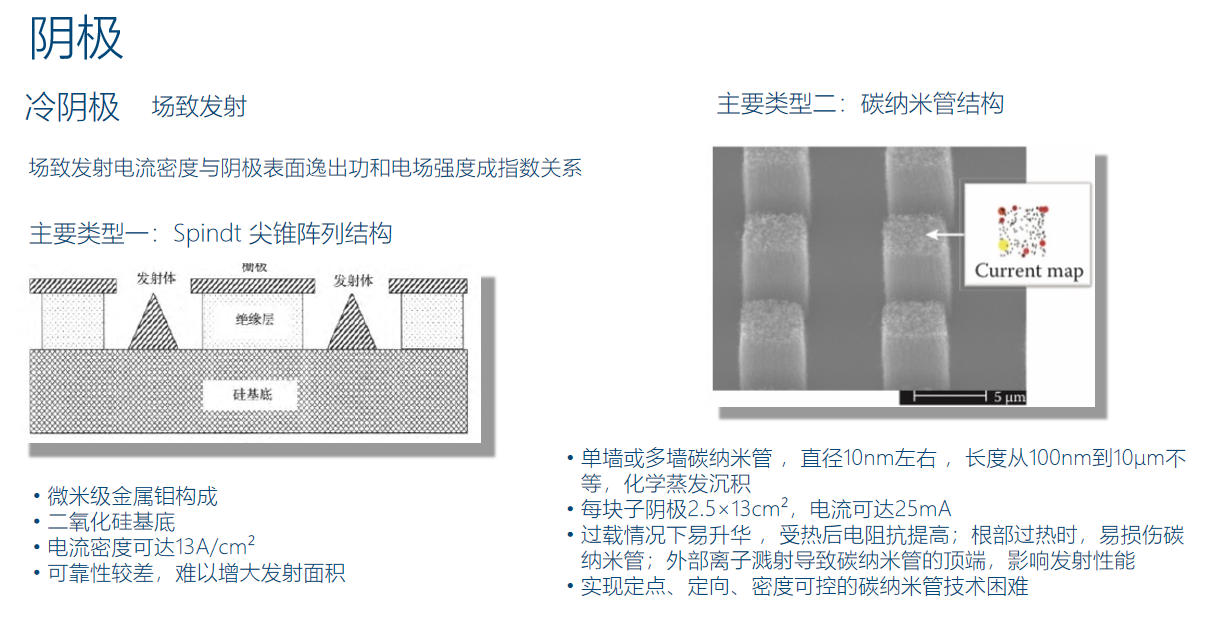
At present, Nanox, which is still in its prime, uses an improved version of the “Spindt cone array” for its cold cathode, without any fundamental technological innovation. To sum up,"Cold cathode" is a field worthy of attention.